Telling little fibs leads down a slippery slope to bigger lies — and Watch Ava Onlineour brains adapt to escalating dishonesty, which makes deceit easier, a new study shows.
Neuroscientists at the University College London's Affective Brain Lab put 80 people in scenarios where they could repeatedly lie and get paid more based on the magnitude of their lies. They said they were the first to demonstrate empirically that people's lies grow bolder the more they fib.
The researchers then used brain scans to show that our mind's emotional hot spot — the amygdala — becomes desensitized or used to the growing dishonesty, according to a study published online Monday in the journal Nature Neuroscience.
"You can think of this as a slippery slope with what begins as small acts of dishonesty escalating to much larger ones," said study lead author Neil Garrett, now a neuroscience researcher at Princeton University. "It highlights the potential dangers of engaging in small acts of dishonesty on a regular basis because these can escalate to much larger ones further down the line."
And during this lying, brain scans that show blood supply and activity at the amygdala decrease with increasing lies, said study co-author and lab director Tali Sharot.
"The more we lie, the less likely we are to have an emotional response" — say, shame or guilt — "that accompanies it," Sharot said.
"The more we lie, the less likely we are to have an emotional response."
Garrett said he suspects similar escalation factors happen in the "real world," which would include politics, infidelity and cheating, but he cautioned that this study was done in a controlled lab setting so more research would be needed to apply it to other situations.
University of Massachusetts psychology and brain sciences professor Robert Feldman wasn't part of the study but praised it: "The results provide clues as to how people may become more convincing liars with practice, and it clearly suggests the danger of tolerating small, white lies, which can escalate into greater and greater levels of deception."
Garrett, Sharot and colleagues arranged for 80 people to go through an experiment where they would see a photo of a jar full of pennies. The subject would advise a partner in another room — someone who was looking at a photo that was less clear — how much money they should guess was in the jar. But the more the partner overestimated the bonus, based on the subject's advice, the higher the reward.
The researchers did a couple variations of the experiment. In one version the test subject was told he and the partner would share in overestimating rewards; in that case, the subject's lies were even bigger.
But in another scenario, the test subject would benefit more from overestimating and the partner would benefit less.
That second scenario showed the increase in the magnitude in lying. The people went from lying on average worth 4 British pounds (about $5) at the beginning to about 8 pounds ($10) near the end of about 80 repetitions — thus going from "little lies to bigger and bigger lies," Sharot said.
And of those 80 test subjects, 25 of them, chosen randomly, did their estimates while an MRI machine scanned their brain. It showed how we get used to the lying, much like someone no longer noticing the smell of their own perfume over time and thus using more, Sharot said.
It shows people's brains adapting to their own wrongdoing. It was so noticeable that the researchers were able to predict growing dishonesty based on the dropping activity in the amygdala.
This Tweet is currently unavailable. It might be loading or has been removed.
Shaul Shavi, who runs the Behavioral Ethics Lab at the University of Amsterdam, said scientists had long suspected this slippery slope in lying existed, but there was limited proof until this "elegant" and "important" study. And the brain scan showing a neurological link with increased lying is novel, added Maurice Schweitzer, who studies deception at the University of Pennsylvania's Wharton School of Business.
The study found that there is a segment of people who don't lie and don't escalate lies, but Sharot and Garrett weren't able to determine how rare those honest people are. It also found that people lie more when it benefits both them and someone else than when they just profit alone.
"That's sort of a good thing," Sharot said.
 Keeping Hope Alive
Keeping Hope Alive
 Honor launches its super
Honor launches its super
 Duke vs. Clemson basketball livestreams: Game time, streaming deals, and more
Duke vs. Clemson basketball livestreams: Game time, streaming deals, and more
 Terrance Hayes’s Soundtracks for Most Any Occasion by Terrance Hayes
Terrance Hayes’s Soundtracks for Most Any Occasion by Terrance Hayes
 Today's Hurdle hints and answers for April 23, 2025
Today's Hurdle hints and answers for April 23, 2025
 Have a Carrot: Picture Books by The Paris Review
Have a Carrot: Picture Books by The Paris Review
 The Last Furriers by Ann Manov
The Last Furriers by Ann Manov
 Have a Carrot: Picture Books by The Paris Review
Have a Carrot: Picture Books by The Paris Review
 Shop Owala's Memorial Day Sale for 30% off tumblers
Shop Owala's Memorial Day Sale for 30% off tumblers
 Love, Loosha by Lucia Berlin and Kenward Elmslie
Love, Loosha by Lucia Berlin and Kenward Elmslie
 Best iPad deal: Save $100 on 13
Best iPad deal: Save $100 on 13
 A guide to Trump's alarming cabinet full of climate deniers
A guide to Trump's alarming cabinet full of climate deniers
 FSU vs. UNC basketball livestream: Game time, streaming deals
FSU vs. UNC basketball livestream: Game time, streaming deals
 UK vs. Arkansas basketball livestreams: Game time, streaming deals, and more
UK vs. Arkansas basketball livestreams: Game time, streaming deals, and more
 Exceptionally rare radio sources detected in the distant universe
Exceptionally rare radio sources detected in the distant universe
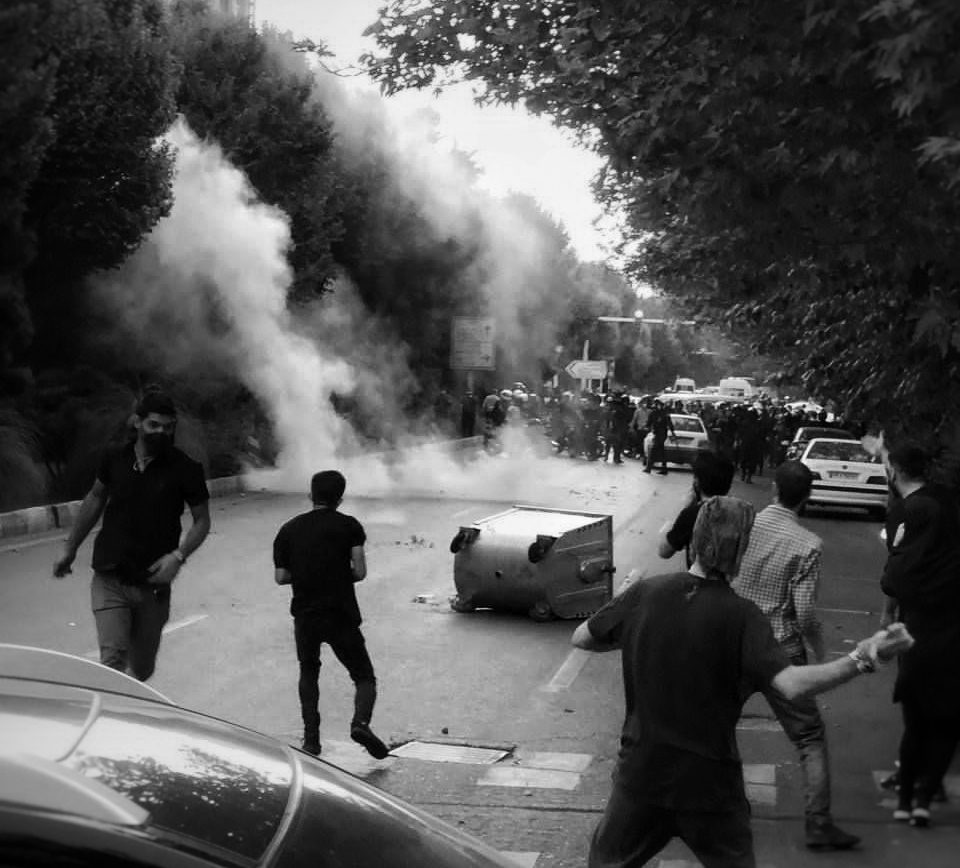 Notes from Iran by Nilo Tabrizy
Notes from Iran by Nilo Tabrizy
 iOS 17.4 beta adds 118 new emoji. The phoenix one is fire.
iOS 17.4 beta adds 118 new emoji. The phoenix one is fire.
 Researchers bid farewell to 'Granny,' the world's oldest known orca
Researchers bid farewell to 'Granny,' the world's oldest known orca
 Best JBL deal: Save $80 on JBL Xtreme 4 portable speaker
Best JBL deal: Save $80 on JBL Xtreme 4 portable speaker
 Taylor Swift deepfakes have gone viral. How does this keep happening?
Taylor Swift deepfakes have gone viral. How does this keep happening?
Marian Blue, the Color of Angels, Virgins, and Other Untouchable ThingsStaff Picks: Strip Clubs, Lightning Rods, and Extramarital AffairsInside Dawn Clements’s Studio by Eileen TownsendUFO Drawings from the National ArchivesWilla Cather, PioneerCooking with Alexandre DumasWhy the French Love Horses by Chantel Tattoli2018 Whiting Awards: Patrick Cottrell, FictionSugimoto's Portraits Bring the Dead Back to LifeIncarnadine, the Bloody Red of Fashionable Cosmetics and Shakespearean PoeticsTo the Future Readers of Lucie BrockDarcy and Elizabeth Go to Summer Camp by Ted ScheinmanOde to JoyRedux: Luisa Valenzuela, Gordon Lish, Thomas Healy2018 Whiting Awards: Nathan Alan Davis, DramaDrue Heinz, 1915–2018 by The Paris Review2018 Whiting Awards: Rickey Laurentiis, PoetryInside Dawn Clements’s Studio by Eileen Townsend2018 Whiting Awards: Tommy Pico, PoetryA Homework Assignment from W. H. Auden Elon Musk will answer questions from Twitter employees Donald Trump writes unusual op How to watch the 2022 Westminster Kennel Club Dog Show Chris Evans' response to those Disney pics of him looking photoshopped is A+ Amazon will launch its drone delivery service later this year Google to pay $118 million settlement of pay equity case A hospital made a Spotify playlist of hot jams to help you perform CPR The 'Same Energy' meme oddly makes perfect sense Emotional support squirrel gets kicked off airplane El Salvador loses half its investment in Bitcoin as crypto plunges 8 best gardening apps, so you can stop killing all of your plants Descendant of Robert E. Lee rebukes Trump for praise of ancestor 'The Quarry' review: Why AAA narrative horror games matter 'Tuble' is 'Wordle' for London Underground experts 15 political Halloween costumes that aren't Donald Trump J.K. Rowling's response to this tweet about Quidditch gets very brutal, very fast Netflix's free walking tours show you where your favourite series are made Cara Delevingne rocks up to royal wedding in suit and top hat, everyone else go home Fitbit Versa review: Excellent fitness tracker, mediocre smartwatch Review: Heated lash curler from Lash Star works... kinda?
2.4038s , 10132.578125 kb
Copyright © 2025 Powered by 【Watch Ava Online】,Unobstructed Information Network